An autoimmune disease is a condition in which your immune system mistakenly attacks your body.
The immune system normally guards against germs like bacteria and viruses. When it senses these foreign invaders, it sends out an army of fighter cells to attack them.
Normally, the immune system can tell the difference between foreign cells and your own cells.
In an autoimmune disease, the immune system mistakes part of your body, like your joints or skin, as foreign. It releases proteins called autoantibodies that attack healthy cells.
Doctors don’t know exactly what causes the immune-system misfire. Yet some people are more likely to get an autoimmune disease than others.
Until recently, treatments addressed only the symptoms of the diseases and aimed at reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune system from attacking self. Modern diagnostic developments in medicine now allow for a causal treatment of chronic and autoimmune diseases.
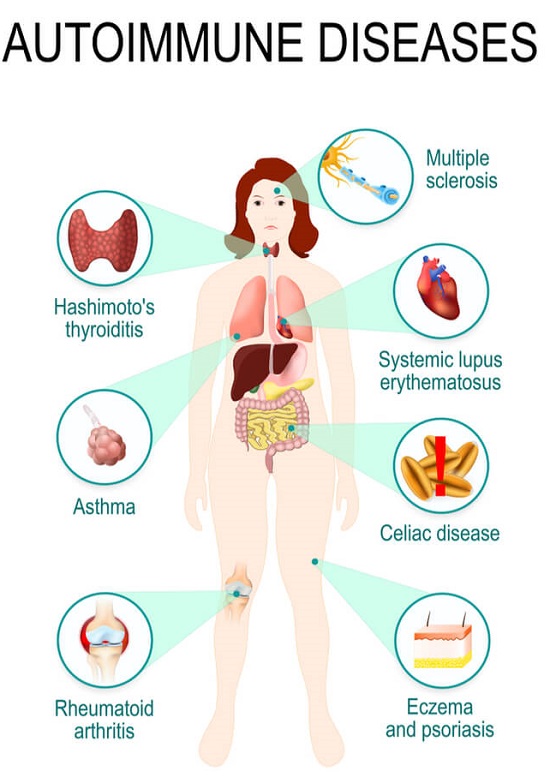
The human body is a biological system that operates under very specific conditions. It consists of cells that aggregate to form organs and, finally, a human body. The operating condition of our cells reflects our general health state.
Factors such as the environment, nutrition, oxygen concentration, water, and micro-nutrients like vitamins, amino acids, proteins, and enzymes, the intake of fats and carbohydrates, are necessary in exact proportions for the healthy functioning of the cells, the building blocks of the body.
An appropriate treatment is one of the greatest benefits for the health and well-being of patients.
Sources: